Understanding Relevant Practical Experience and its role in the CA qualification

Learn more about the Relevant Practical Experience (RPE) undertaken by ICAS students and why it’s key to the CA qualification.
What is Relevant Practical Experience (RPE)?
RPE is a key component of the CA qualification, and a compulsory requirement for students to qualify and be eligible for ICAS membership.
 Combined with study, RPE supported by the employer creates a learning environment to develop the relevant technical skills, attitudes, and ethics of a CA. It’s therefore important that students receive practical workplace training to operate competently before they can become a qualified CA.
Combined with study, RPE supported by the employer creates a learning environment to develop the relevant technical skills, attitudes, and ethics of a CA. It’s therefore important that students receive practical workplace training to operate competently before they can become a qualified CA.
The International Federation of Accountants stipulates that practical experience must be gained by students and must be complete before they qualify as accountants.
What’s the role of the ATO in RPE?
The ATO plays a pivotal role in monitoring a student’s practical training and helping to prepare them for qualification and becoming a future member of ICAS. In delivering practical training, the ATO ensures that:
- Students can seek guidance and advice on matters relating to their practical training.
- Students practical training is properly monitored, guided and verified.
- The working environment is such that students develop the professional and ethical attitudes expected of ICAS members.
RPE must include sufficient exposure to the nature of the role, undertaking the real-life work of a financial organisation. The range of RPE is determined by factors such as a complexity and variety of tasks fit for purpose, as well as the level of supervision and support.
RPE responsibilities
Students’ responsibilities
Students are required to actively participate in structured opportunities and authentic work-based activities. This should include but isn’t limited to:
- Demonstrating commitment by showing up and keeping promises.
- Contributing to tasks and engaging in discussion.
- Understanding their employer’s values and goals.
- Taking responsibility for their own actions.
- Seeking constructive feedback and demonstrating proactive listening.
ATOs’ responsibilities
ATOs are authorised by ICAS to provide RPE and are expected to ensure that:
- Students receive sufficient RPE to meet the ICAS competency requirements for the development of technical and non-technical skills and to enable them to effectively apply these to a variety of relevant practical situations.
- Students are appropriately supervised, mentored and coached throughout the training period by professionally qualified staff to ensure they meet the work-experience requirements and are prepared for the education and examination programme.
- Students have exposure to a reasonable mix of accounting work that aligns with the competencies, so they can obtain the appropriate range of practical experience.
- Those persons appointed with responsibility for supervising, coaching, supporting and signing off the logbook have appropriate technical knowledge and skills to perform these roles.
- Methods are implemented to assess student competence, with clear criteria and procedures in place for students to be assessed as competent.
- Students receive structured practical experience by establishing a documented and regularly monitored work experience for all students undertaking RPE.
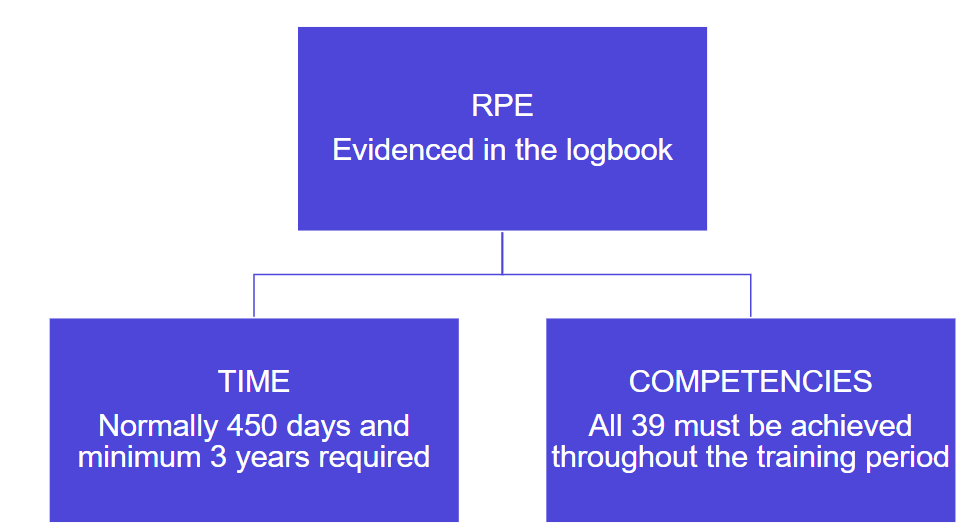
The three elements of RPE
The areas of RPE are defined by three elements:
- RPE
- Time
- Competencies
The logbook
Students record and evidence their RPE time and the competencies they have attained in their logbook.
The student’s counselling member or reviewer is responsible for approving all these logbook entries.
And the student’s assigned counselling member also has responsibility for the logbook's final review and sign-off.
RPE time
The student’s training contract is the approved period in which they’ll gain their RPE and is normally a minimum of 3 years (1095 days). During this period students must normally evidence and record in their logbook a minimum of 450 days of RPE.
One working day is equivalent to 7 hours. If additional hours are worked on a particular day, these should be recorded as overtime and will still count towards the total number of days worked.
Time is recorded in the logbook as follows:
- Employment days (automatically calculated in the logbook based on the student’s employment start date).
- RPE (recorded by the student).
- Statutory audit (recorded by the student).
- Other accepted audit (recorded by the student).
Statutory audit and other accepted audit are categorised separately within the logbook but count towards the overall minimum RPE requirements. You'll find more information in our counselling member's guide to the Audit Qualification.
Our logbook follows FRC guidelines and requires all students to record a minimum of 450 days of RPE over 3 years.
This also applies to those on alternative routes (such as the school leaver route and RGU Graduate Apprenticeship route) who were previously required to record more than 450 days of RPE.
The training contract is at the employer’s discretion, so you can choose whether students are required to complete an approved period of more than 3 years as part of their training contract.
RPE competencies
A competency is the ability to perform a work role or task to a demonstrated defined standard.
From an ICAS perspective, they’re the skills that a student develops in particular areas during the period of their training contract.
The CA qualification requirements include 39 core competencies, which must be completed during the training contract. These are split into six timelines:
- Ethics and Integrity.
- Technical Competence (Accounting Technical competence & Data and Technology EC combined).
- Communications.
- Teamwork and Leadership.
- Personal Effectiveness.
- Problem Solving and Decision Making.
When can a competency be achieved?
Competency achievement is dependent on the scenarios and experience gained by each student individually, these dependencies will affect the timing of when competencies can be achieved and will vary student to student.
Competencies can start to be achieved in the student’s first year of training, with the earlier competencies within each timeline targeted at the entry level and the later competencies more advanced.
Competencies should only be achieved when a student can demonstrate they have acquired the skills and can perform them at a consistent level.
Recording competencies in the logbook
Upon completing a competency, a student is required to record it in their logbook and submit it for approval. They'll need to provide supporting commentary in the form of a short (50 to 200-word) reflective statement.
The reflective statement must provide the reviewer with sufficient evidence to allow them to confirm if the competency has been achieved to the required standard.
An employer’s guide to the logbook
In our practical guide to the logbook, we explain more about the key logbook roles, the key responsibilities and how to perform them.